Learning programming languages is a good option to find a good job. Above all, if you dedicate yourself to this. Because for no one is a secret that we live in times where many applications are used. That’s why this post will teach you how to install Rust on OpenSUSE 15.2
What is Rust?
Rust is an open source, multipurpose and new programming language that aims to retire to the C language. Although it is sponsored by Mozilla and Samsung, it is a community project. Its focus is primarily on large programs that run on the client and server side.
The main characteristics of Rust are performance, reliability, and productivity. Rust can compile and create applications very quickly; it is conducive to very few failures and its large documentation makes it possible to learn quickly.
Install Rust on OpenSUSE 15.2
Perhaps the best way to get Rust on OpenSUSE is through the official installer provided by the language. In this respect, this guarantees that we are running the latest version available and is not complicated.
To do this, open a terminal or connect via SSH and update OpenSUSE.
sudo zypper up
After this, make sure you have the curl package installed on the system
sudo zypper in curl
And all you have to do is run this command which will download and install Rust on your system
curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
During the installation, you will be asked how to install it. It is recommended that you use the default configuration by choosing option 1.
At the end you will get an output screen similar to this one:

And to make rust available in the terminal without problems, run:
source $HOME/.cargo/env
Finally, you can check the version we just installed.
rustc --version rustc 1.50.0 (cb75ad5db 2021-02-10)
Testing Rust on OpenSUSE 15.2
Now it is necessary to make a test file and run it to make sure that everything is OK.
So, create the project folder and inside it the program folder. You can choose any name you want.
mkdir ~/projects cd projects mkdir example cd example
Now we just need to add some rust code to the file. A hello world!! will suffice.
nano helloworld.rs
And add the following:
fn main() {
println!("Hello, thanks for visiting Osradar blog.");
}
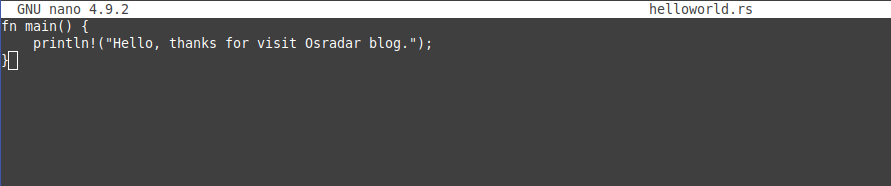
Save your changes and close the editor.
Then, compile the file with the rustc command
rustc helloworld.rs
And now run it
./helloworld
Finally, you get the following output, which indicates that Rust is now working properly.

Hello, thanks for visit Osradar blog.
So, enjoy it.
Conclusion
Installing the Rust language in Linux is a fairly simple process. The possibilities offered by this language are many. It is also a great alternative to traditional programming languages.



