Thanks to the internet and computers in general, education is now better. In addition, it allows arriving in a faster way and of better quality. So, if you are a teacher or run an education center, then this post on how to install Moodle on CentOS 7 is ideal for you.
Moodle is a learning management system (LMS). It is quite popular in the world and is the main online learning tool for many educational institutions. It is written in PHP and supports several web servers such as Apache and Ngnix.
One of its main advantages is that it is open source and has a very active user and developer community that allows you to keep track of the development and its news.
So, let’s install Moodle on CentOS 7.
0. Prerequisites
Before starting you should do a few things so that there are no problems during the installation. First, install some necessary packages:
:~# yum install nano wget yum-utils
Next, disable SELinux:
:~# nano /etc/selinux/config
And change SELinux to disable:

Finally, reboot the system.
1. Upgrade the system
First, you need to update the system. It is really simple to do and with this you guarantee to have the system with the security patches installed and working.
:~$ su :~# yum update

Now, you can go on.
2. Install Apache Web server
As I said before, Moodle is compatible with several web servers, however, I will use Apache’s httpd. It’s a pretty well known server and it’s really easy to use.
To install it run this command.
:~# yum install httpd

Now, enable and start the service.
:~# systemctl enable httpd :~# systemctl start httpd

Add the rule for the firewall.
:~# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
And that’s all for Apache.
2. Install PHP
PHP is a programming language for web applications. Moodle is written in this fantastic language so you have to install it.
We only have one detail, the version that comes in the official CentOS 7 repositories is very old and Moodle requires something newer. So I will use an external repository to install PHP 7.1.
:~# yum install epel-release :~# rpm -Uhv https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm :~# yum-config-manager --enable remi-php71


Then, install PHP 7.1
:~# yum install php php-common php-intl php-zip php-soap php-xmlrpc php-opcache php-mbstring php-gd php-curl php-mysql php-xml

So, restart Apache.
:~# systemctl restart httpd
PHP is correctly installed.
3. Install and configure MariaDB
The next step is to install and configure MariaDB. Moodle requires a database manager. In this case I will use MariaDB, an open source and easy to install MySQL fork.
:~# yum install mariadb mariadb-server

Now, you need to enable and start the service.
:~# systemctl enable mariadb :~# systemctl start mariadb

Then, it is necessary to define the root password for MariaDB. This is easy to do thanks to the mysql_secure_installation script.
:~# mysql_secure_installation

In this section, you will be asked other questions concerning the configuration of MariaDB. These are the questions and so I have answered. So, you can do it as you wish. They are basic configurations.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] N Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
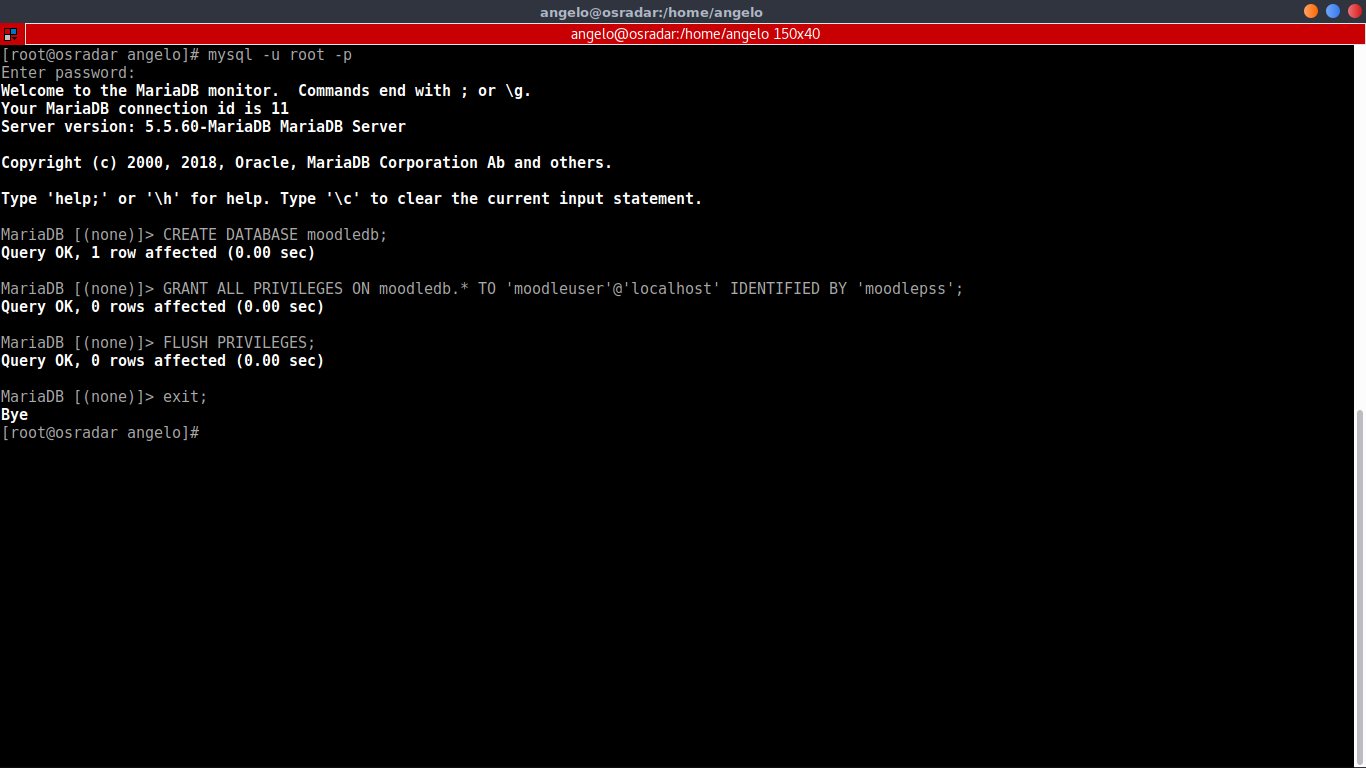
So, the next step is to create the Moodle database.
:~# mysql -u root -p CREATE DATABASE moodledb; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON moodledb.* TO 'moodleuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'moodlepss'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; exit;
Finally, you need to edit the file /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf and add the following.
:~# yum install nano :~# nano /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4 [mysqld] innodb_file_format = Barracuda innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_large_prefix character-set-server = utf8mb4 collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci skip-character-set-client-handshake [mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4

For these changes to take effect, restart MariaDB.
:~# systemctl restart mariadb
4.- Install Moodle
It’s finally time to install Moodle. First, you have to download it.
:~# cd /tmp/ :~# wget https://download.moodle.org/download.php/direct/stable35/moodle-latest-35.tgz -O moodle-latest.tgz

Then, decompress it.
:~# tar -xvzf moodle-latest.tgz
Next, move the created folder to /var/www/html.
:~# mv moodle /var/www/html/
Now it is necessary to change the owner of the folder. This to avoid permission problems.
:~# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/

5. Create a virtual host for Moodle
You need to create a virtual host for Moodle. It’s simple. Run this command and add the following.
:~# nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/moodle.conf

Then, restart Apache.
:~# systemctl restart httpd
6. Complete the Moodle installation from CLI
Now is the time to complete the installation from CLI. To do this, run:
:~# /usr/bin/php /var/www/html/moodle/admin/cli/install.php

During the execution of the script, you will first be asked for the language for the installation. The rest are database parameters and paths. See the images for reference.

Note: It is not mysqli. It is mariadb option on database driver.
You have also to set the admin account.

Finally, you will see this.

If you make a mistake, you can continue. In the end, you delete the /var/www/html/moodle/config.php file and run the installer again.
Next, give permission to the config file.
:~# chmod o+r /var/www/html/moodle/config.php
And restart apache.
:~# systemctl restart httpd
Now, go to your moodle directory on your web browser.
Next, log in. Go to http://your-domain/login.

And finally, you will see this.

And that’s it.
Conclusion
Now that you know how to install Moodle you can start creating your own learning platforms.
One piece of advice I give you is to read through each step carefully.
Please share this article on your social networks.



